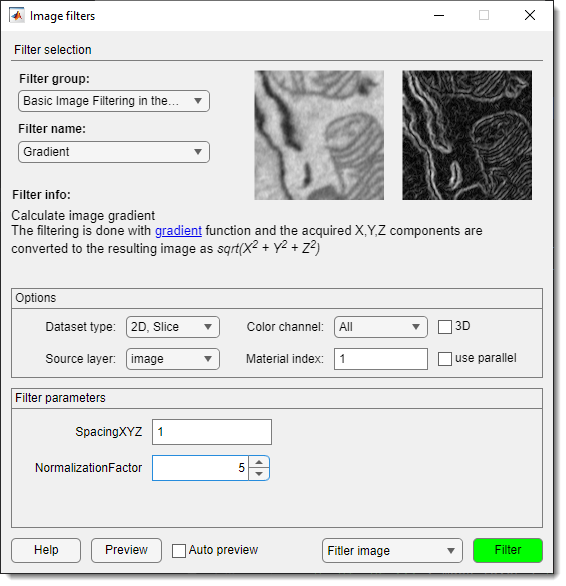
Image Filters Dialog
Back to MIB | User interface | Menu | Image
Overview
Collection of image filters arranged into four categories:
- Basic image filtering in the spatial domain
- Edge-preserving filtering
- Contrast adjustment
- Image binarization
Options
Prior to filtering images, the following options may be tweaked:
- : specify whether filtering applies to the shown slice, current 3D stack, or the whole dataset.
- : select the layer to be filtered (e.g., Image, Selection, Mask, Model).
- : choose a specific color channel, all shown channels, or all channels in the image.
- : index of material to filter (available when Source layer is Model).
- : apply a 3D filter.
The filtered image can be post-processed using a dropdown at the bottom of the dialog:
- Filter image: filter and display the result.
- Filter and subtract: filter and subtract the result from the unfiltered image.
- Filter and add: filter and add the result to the unfiltered image.
Basic image filtering in the spatial domain
Average filter
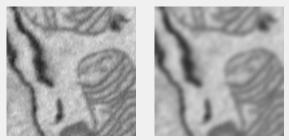
Averages image signal using a rectangular filter. Uses MATLAB’s imfilter with the average filter from fspecial.
Supports: 2D/3D
Circular averaging filter (pillbox)

Averages image signal using a disk-shaped filter. Uses imfilter with the disk filter from fspecial.
Supports: 2D
Calculates a distance map from seeds in the Source Layer (Selection, Mask, or Material).
2D uses bwdist with four options for distance calculations;
3D uses bwdistsc "euclidean" only, by Yuriy Mishchenko.
Supports: 2D/3D
Elastic distortion filter
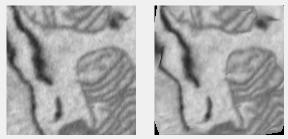
Applies elastic distortion based on Simard et al., "Best Practices for Convolutional Neural Networks Applied to Visual Document Analysis" (link). See also StackOverflow and Elastic Distortion Transformation by David Franco.
Supports: 2D
Entropy filter
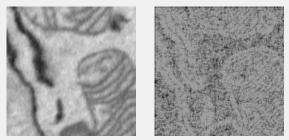
Local entropy filter; each pixel shows entropy (-sum(p.*log2(p)), where p is normalized histogram counts) of its neighborhood. See entropyfilt.
Supports: 2D
Frangi filter
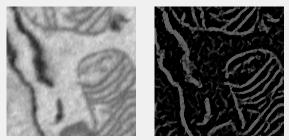
Enhances elongated or tubular structures using Hessian-based multiscale filtering. Uses fibermetric.
Supports: 2D/3D
Gaussian smoothing filter
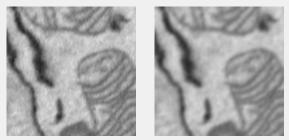
Rotationally symmetric Gaussian lowpass filter with size (Hsize) and standard deviation (Sigma). 2D uses imgaussfilt; 3D uses imgaussfilt3.
Supports: 2D/3D
Gradient filter
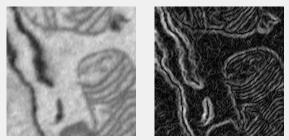
Calculates image gradient using gradient. Result combines X, Y, Z components as sqrt(X^2 + Y^2 + Z^2).
Supports: 2D/3D
Laplacian of Gaussian filter
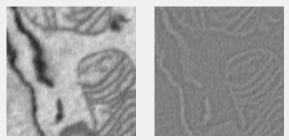
Highlights edges using the Laplacian of Gaussian filter. Converted to unsigned integers with a NormalizationFactor. Uses imfilter with the log filter from fspecial.
Supports: 2D/3D
Mathematical operations
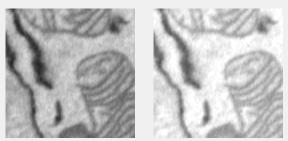
Applies standard operations (add, subtract, multiply, divide) to the image, with optional class conversion.
Supports: 2D
Mode filter (R2020a or newer)
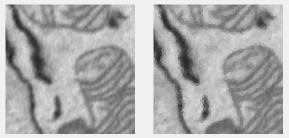
Each pixel shows the mode (most frequent value) in its neighborhood. Uses modefilt.
Supports: 2D/3D
Motion filter
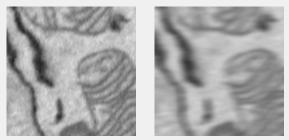
Applies motion blur. Uses imfilter with the motion filter from fspecial.
Supports: 2D
Prewitt filter
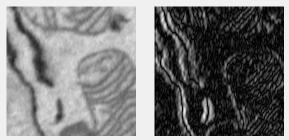
Enhances edges using the Prewitt method. Uses imfilter with the prewitt filter from fspecial.
Supports: 2D/3D
Range filter
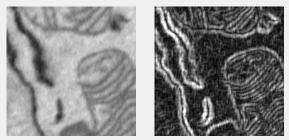
Local range filter; each pixel shows the range (max - min) of its neighborhood. See rangefilt.
Supports: 2D/3D
Salt and pepper filter
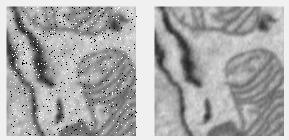
Removes salt & pepper noise using a median filter, then removes pixels above an IntensityThreshold based on the difference.
Supports: 2D
Sobel filter
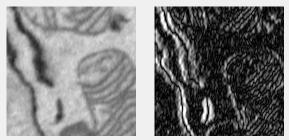
Enhances edges using the Sobel method. Uses imfilter with the sobel filter from fspecial.
Supports: 2D
Std filter
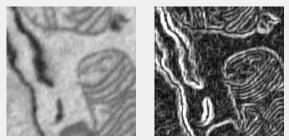
Local standard deviation filter; each pixel shows the standard deviation of its neighborhood with symmetric padding. See stdfilt.
Supports: 2D
Edge-preserving filtering
Remove noise while preserving object edges using one of the following filters.
Anisotropic diffusion filter
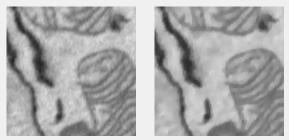
Edge-preserving anisotropic diffusion with the Perona-Malik algorithm. Uses imdiffusefilt.
Supports: 2D
Bilateral filter
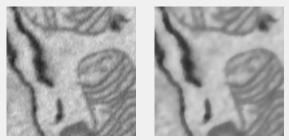
Edge-preserving bilateral filtering with Gaussian kernels. Uses imbilatfilt.
Supports: 2D
DNNdenoise filter
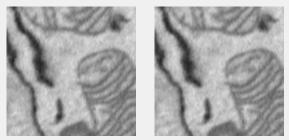
Denoises using a deep neural network. Uses denoiseImage.
Supports: 2D
Median filter
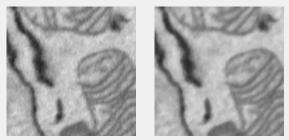
Median filtering; each pixel shows the median value in its neighborhood. 2D uses medfilt2; 3D uses medfilt3.
Supports: 2D
Non-local means filter
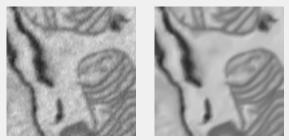
Uses imnlmfilt for non-local means filtering.
Supports: 2D
BMxD filter
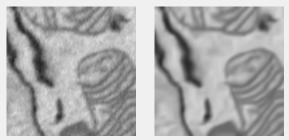
Uses block-matching (BM3D v2.01) and 3D collaborative ((BM4D v3.2)) filtering. Licensed for non-profit use only.
See installation details in System requirements.
Supports: 2D
BM3D and BM4D References
- [BM3D] K. Dabov, A. Foi, V. Katkovnik, and K. Egiazarian, Image Denoising by Sparse 3D Transform-Domain Collaborative Filtering, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 16, no. 8, August, 2007. preprint at http://www.cs.tut.fi/~foi/GCF-BM3D.
- [BM4D] M. Maggioni, V. Katkovnik, K. Egiazarian, A. Foi, "A Nonlocal Transform-Domain Filter for Volumetric Data Denoising and Reconstruction", IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 119-133, January 2013. doi:10.1109/TIP.2012.2210725
- [BM4D] M. Maggioni, A. Foi, "Nonlocal Transform-Domain Denoising ofVolumetric Data With Groupwise Adaptive Variance Estimation", Proc. SPIE Electronic Imaging 2012, San Francisco, CA, USA, Jan. 2012.
Contrast adjustment
Filters intended to adjust image contrast.
Add noise filter
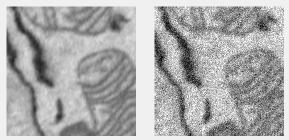
Adds noise using imnoise. Options:
- Gaussian: Gaussian white noise
- Poisson: Poisson noise from the data
- Salt & pepper: Adds salt and pepper noise
- Speckle: Multiplicative noise (J = I + n*I, n is uniform random noise, mean 0, variance 0.05)
Supports: 2D
Fast Local Laplacian filter
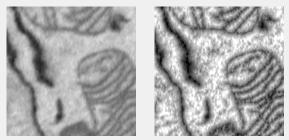
Enhances contrast, removes noise, or smooths details. Uses locallapfilt.
Supports: 2D
Flat-field correction

Corrects grayscale or RGB images using Gaussian smoothing (sigma) to approximate shading. Uses imflatfield.
Supports: 2D
Local Brighten filter
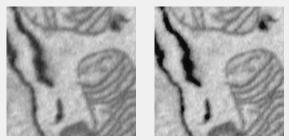
Brightens low-light images. Uses imlocalbrighten.
Supports: 2D
Local Contrast filter
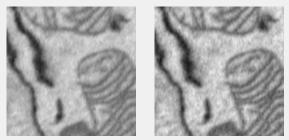
Edge-aware local contrast manipulation. Uses localcontrast.
Supports: 2D
Reduce Haze filter
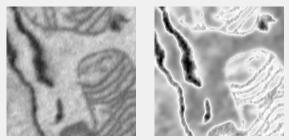
Reduces atmospheric haze. Uses imreducehaze.
Supports: 2D
Unsharp mask filter
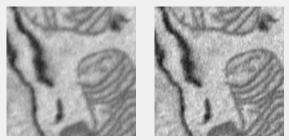
Sharpens by subtracting a blurred version from the original. Uses imsharpen.
Supports: 2D
Image binarization
Filters that process the image and generate a bitmap mask, assignable to the Selection or Mask layers via the .
Edge filter
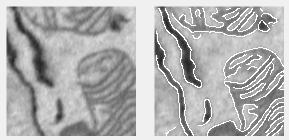
Finds edges in intensity images using edge.
Supports: 2D
- Approxcanny: Faster, less precise Canny approximation
- Canny: Uses two thresholds for strong/weak edges, less noise-sensitive
- Log: Finds zero-crossings with Laplacian of Gaussian
- Prewitt: Uses Prewitt derivative approximation
- Roberts: Uses Roberts derivative approximation
- Sobel: Uses Sobel derivative approximation
SLIC clustering filter
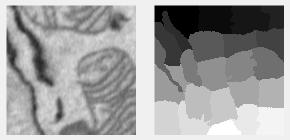
Clusters pixels by intensity using the SLIC algorithm.
Supports: 2D
- : approximate size of each cluster in pixels
- : 100 (square) to 0 (flexible)
- : number of horizontal blocks for memory efficiency
- : number of vertical blocks
SLIC References
- Radhakrishna Achanta, Appu Shaji, Kevin Smith, Aurelien Lucchi, Pascal Fua, and Sabine Süsstrunk, SLIC Superpixels Compared to State-of-the-art Superpixel Methods, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 34, num. 11, p. 2274 – 2282, May 2012.
- Radhakrishna Achanta, Appu Shaji, Kevin Smith, Aurelien Lucchi, Pascal Fua, and Sabine Süsstrunk, SLIC Superpixels, EPFL Technical Report no. 149300, June 2010.
Watershed clustering filter
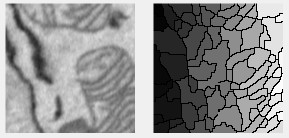
Clusters pixels based on ridges using the watershed algorithm.
Supports: 2D
- : assign results to MIB layers
- : larger values yield bigger clusters
- : "black-on-white" (electron microscopy) or "white-on-black" (light microscopy)
- : preserve or fill ridge gaps
- : "clusters" or "ridges"
Back to MIB | User interface | Menu | Image